Leave Your Message
-
Phone
-
E-mail
Cold forging is a critical manufacturing process, and the Cold Forging Die plays a pivotal role in it. This technique is known for producing complex shapes with exceptional precision. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global cold forging market is projected to reach $12.5 billion by 2027, reflecting its growing importance in various industries.
Industry expert Dr. James Carter emphasizes, "The efficiency of a Cold Forging Die determines the quality and cost-effectiveness of the entire forging process." His statement highlights the necessity of well-engineered dies in producing high-quality components. However, achieving this efficiency is not always straightforward.
The design and maintenance of Cold Forging Dies can be challenging. Factors like material selection and wear resistance significantly impact their performance. Despite advances in technology, issues such as die wear can lead to costly downtimes. Reflecting on these challenges allows manufacturers to optimize processes and improve outcomes. The evolution of Cold Forging Die design remains an area worth exploring.
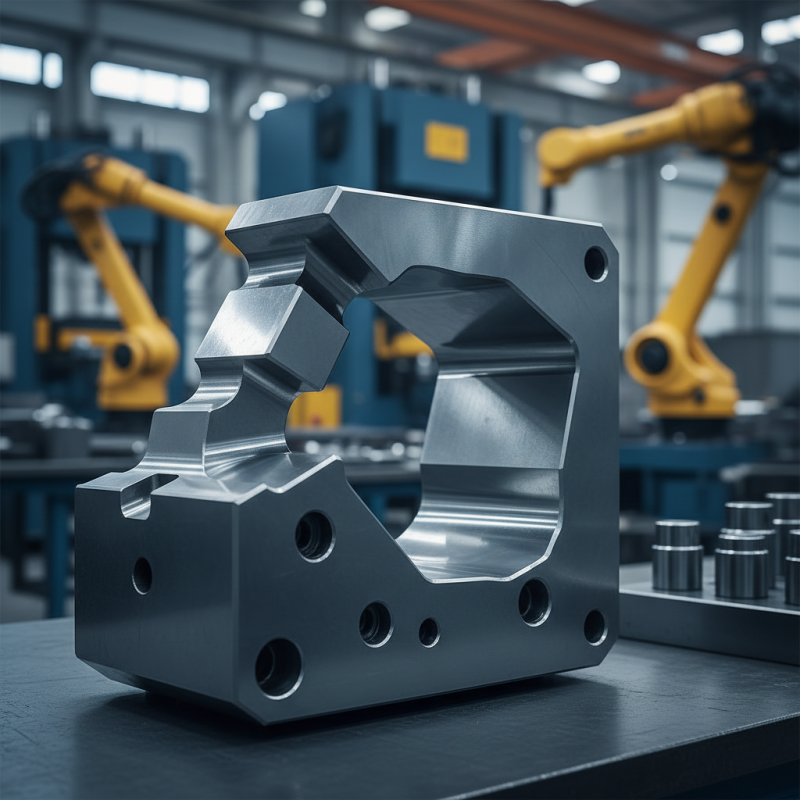

Cold forging die is a critical tool in the manufacturing process. It shapes metal at room temperature, unlike hot forging, which uses heat. This method allows for precise dimensions and a smooth surface finish. The process increases strength due to work hardening, essential for robust components. The die itself is engineered to withstand high pressures and is carefully designed to create specific shapes.
When designing cold forging dies, precision is key. Small mistakes can lead to defects. The material choice for the die significantly impacts its lifespan and performance. Tool steels are often used, as they provide durability. However, the cost of high-quality materials can be a barrier for some.
Tips: Always conduct thorough testing before full-scale production. Monitor the die regularly for wear and tear. Regular maintenance can extend the die’s life, preventing costly failures. Balancing quality and cost remains a challenge in this industry. Understanding the limitations of tooling can lead to better design choices in the future.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Material | High carbon steel or tool steel, often treated for durability |
| Process Temperature | Typically below the recrystallization temperature of the metal |
| Common Applications | Automotive components, fasteners, and precision parts |
| Advantages | Improved strength, tighter tolerances, and less material waste |
| Die Types | Open die, closed die, and precision die designs |
| Typical Industries | Manufacturing, aerospace, and electronics |
| Key Considerations | Die material, design complexity, and production volume needs |
Cold forging dies are essential tools in the manufacturing process. They shape metal components at room temperature. Understanding the components of a cold forging die can clarify how it functions.
A cold forging die typically consists of two main parts: the upper die and the lower die. The upper die compresses the metal, forcing it into the desired shape. The lower die acts as a base, providing support during the forging process. These components must be precisely engineered to ensure accuracy and durability. Inadequate design can lead to defects in the final product.
Other important parts include guides and punches. Guides help align the metal and dies, ensuring consistency. Punches deliver force to shape the metal. However, the wear and tear on these components can lead to variations in quality. Manufacturers need to regularly monitor and reflect on their die performance for optimal results.
Cold forging is a widely used metalworking process. It shapes metal at low temperatures, enhancing durability. The process involves placing metal into a die and applying pressure. This pressure forces the material to take the shape of the die.
The cold forging process begins with careful material selection. The metal must have good ductility and flow characteristics. Once prepared, it is heated slightly to reduce brittleness. This helps achieve better results. A series of dies shapes the metal through various stages. Each die has a specific design. The metal flows into these designs, creating desired shapes.
Common applications include automotive and industrial parts. Some challenges may arise. Misalignment of dies can cause defects. Inexperience can lead to poor shapes and increased waste. Each detail should be examined carefully during the process. This continuous improvement is crucial for quality manufacturing. Cold forging is efficient, yet it demands precision and expertise.
The above bar chart illustrates the production efficiency of the cold forging process over the last four years. As we can see, there has been a steady increase in efficiency, showcasing improvements in techniques and technology used in cold forging.
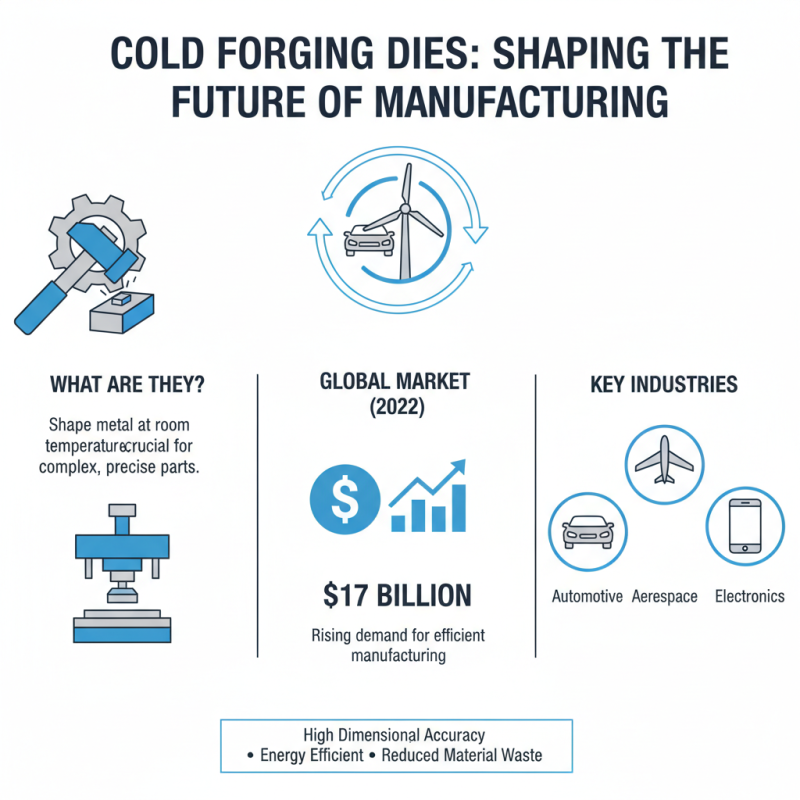
Cold forging dies play a significant role in manufacturing processes across various industries. These dies are designed to shape metal at room temperature. They are crucial for producing complex parts with high dimensional accuracy. In 2022, the cold forging market was valued at approximately $17 billion. This number indicates the rising demand for this efficient manufacturing method.
Applications of cold forging are diverse. Automotive components, such as gears and fasteners, benefit greatly from this process. Reports suggest that automotive applications account for nearly 60% of the cold forging market. The aerospace industry also utilizes cold forging to create lightweight, strong components. These applications require precision and reliability, making cold forging an attractive option.
However, challenges exist. Not all materials are suitable for cold forging. Some metals may crack under pressure. This limits the range of materials that can be processed. The initial cost of producing custom dies can be high, resulting in long lead times for new designs. Manufacturers must weigh these factors against the benefits of faster production and reduced waste. Balancing these elements is crucial for achieving efficiency in manufacturing.
Cold forging dies play a crucial role in modern manufacturing. These tools shape metal at room temperature, allowing for precise and efficient production. One major advantage is increased material strength. The process aligns the metal's grain structure, enhancing durability without the need for extreme heat.
Additionally, cold forging minimizes waste. Traditional methods often involve cutting metal, which leads to scrap. With cold forging, more material is retained, making it a cost-effective solution. However, achieving the ideal conditions for cold forging requires careful calibration. Any misalignment or incorrect pressure can lead to defects in the final product.
Moreover, production speed improves with cold forging. The rapid cycle times increase overall efficiency. Yet, the initial setup can be time-consuming. Finding the right die design may take multiple attempts. Each of these factors plays a role in the decision-making process for manufacturers. Balancing speed and quality can be challenging but ultimately rewarding.






