Leave Your Message
-
Phone
-
E-mail
Cold forging is a widely used manufacturing process that involves shaping metal at low temperatures, allowing for enhanced material properties and precision in production. Central to this process is the **Cold Forging Die**, a specialized tool that plays a critical role in determining the quality and efficiency of metal components. The design and functionality of a cold forging die greatly impact the manufacturing workflow, influencing factors such as production speed, dimensional accuracy, and overall material strength.
In modern manufacturing, understanding the intricate relationship between the cold forging die and the forging process is essential for optimizing production. The die not only helps in forming intricate shapes but also ensures minimum material waste and high performance of the final product. As industries continue to evolve, the need for high-quality, cost-effective manufacturing solutions makes the exploration of cold forging dies increasingly relevant. This introduction will discuss the vital components of cold forging dies and their significant impact on manufacturing processes, providing insights into how they contribute to the advancement of metalworking techniques.
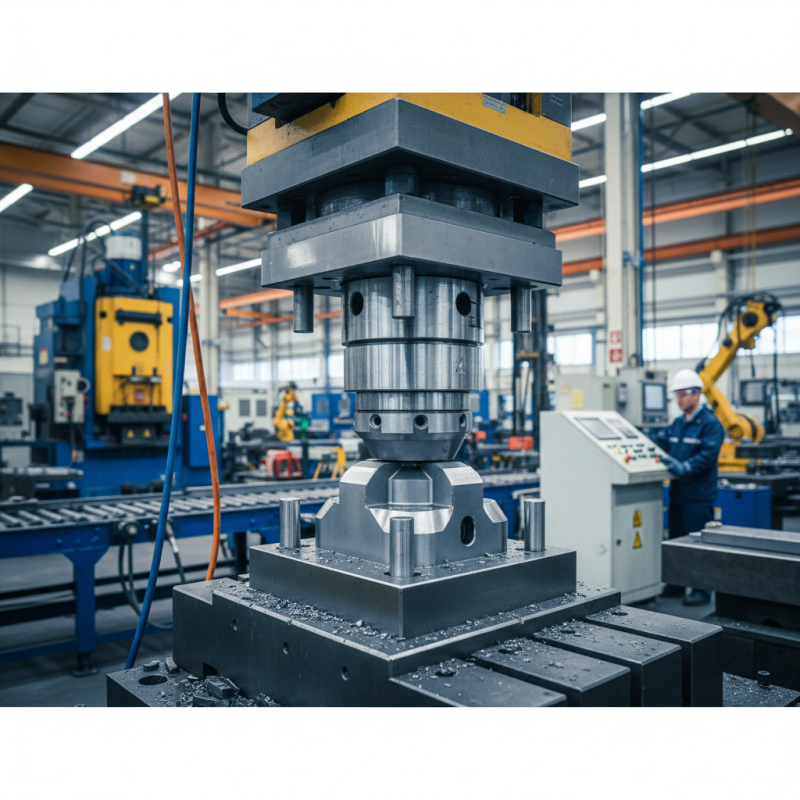

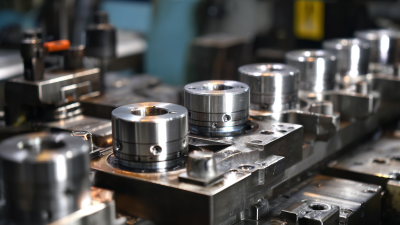
A cold forging die is a crucial tool used in the cold forging process, which shapes metal at room temperature. This method allows for the efficient mass production of complex geometries with increased strength and improved properties. The die is designed to form the metal into a desired shape as it is subjected to high pressure, without the need for extensive heating. This not only preserves the qualities of the metal but also results in minimal material waste and enhanced dimensional accuracy.
One important aspect to consider when working with cold forging dies is their material selection and design. Using durable materials for the die ensures longevity and resilience against wear during production. Additionally, optimizing the die design can significantly reduce the cycle time and improve overall efficiency.
Tips: To achieve optimal results, regularly inspect the dies for any signs of wear or damage. Implement preventative maintenance strategies to ensure consistent performance and longevity. Moreover, collaborating with experienced engineers during the die design phase can lead to innovative solutions that enhance the production process, minimizing downtime and maximizing output.
Cold forging dies are essential tools in the manufacturing process that allow for the precise shaping of metal without the application of heat. These dies are specifically designed to handle the high pressures necessary for deforming materials at room temperature, leading to enhanced mechanical properties and improved surface finish. To achieve optimal performance, cold forging dies consist of several key components, each playing a critical role in the overall efficacy of the forging process.
The primary components of cold forging dies include the die block, punch, and guiding mechanisms. The die block forms the main structure that houses the cavity where the metal is shaped. It is typically made from high-strength materials to withstand the immense forces exerted during forging. The punch is used to exert pressure on the metal, pushing it into the die cavity, and its design must ensure a precise fit and adequately resist wear over time. Additionally, guiding mechanisms are incorporated to maintain alignment during the forging process, preventing misalignment and resulting defects in the finished product.
Other important elements may include the ejector system, which helps remove the forged part from the die after forming, and cooling channels that help manage heat generated during the process. Together, these components work in harmony to ensure efficient operation and consistent quality of the forged parts, ultimately impacting the overall productivity and effectiveness of the manufacturing process.
Cold forging is a manufacturing process that involves shaping metal at room temperature, typically using dies. This method stands out due to its ability to produce high-strength, complex shapes with minimal material waste. According to industry reports, cold forging can achieve tensile strengths exceeding 1,300 MPa, making it beneficial for applications where durability is paramount, such as in aerospace and automotive sectors.
The process begins with the selection of the appropriate die, which is critical for shaping the metal accurately. The raw material, often in the form of a cylindrical billet, is placed into the die, where it is subjected to high pressure. This pressure deforms the metal, conforming it to the die's shape, which leads to a precise final product. Data indicates that cold forging can enhance production efficiency by up to 50% compared to traditional machining, as it requires fewer processing steps and reduces scrap material significantly.
**Tip**: When considering cold forging for your production needs, ensure that the die design is optimized for the specific material you are using. A well-designed die can dramatically enhance production efficiency and improve the quality of the final product. Additionally, monitor the temperature of the workpiece as variations can significantly affect the forging process and the overall integrity of the final product.
Cold forging dies are essential tools in the manufacturing process that significantly enhance productivity and product quality. One of the primary advantages of using cold forging dies is the reduction in material waste. Since the process involves the deformation of metal at room temperature, it minimizes excess scrap compared to traditional machining methods. This not only lowers material costs but also contributes to a more sustainable manufacturing environment.
Another key benefit is the superior mechanical properties achieved through cold forging. The process typically results in a refined grain structure that enhances the strength and durability of the finished products. Parts produced through cold forging exhibit higher tensile strength and improved fatigue resistance, making them ideal for applications in demanding industries such as automotive and aerospace. Additionally, cold forging allows for complex shapes and intricate designs, reducing the need for extensive machining and further streamlining production.
Overall, the adoption of cold forging dies in manufacturing presents a blend of efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and high-quality outputs, making it a preferred choice for many manufacturers aiming to enhance their production capabilities.

Cold forging is a manufacturing process that significantly enhances material properties while improving production efficiency. By deforming metal at lower temperatures, cold forging ensures that the material maintains its integrity and strength. According to a report by the National Institute of Standards and Technology, cold forged parts exhibit up to 30% higher tensile strength compared to similar components produced via hot forging methods. This enhanced strength results from strain hardening during the cold working process, making cold forging a preferred choice for industries demanding high-performance components.
The impact of cold forging on production efficiency is equally compelling. The process often requires fewer machining operations due to the superior shape accuracy and surface finish attained during forging. Research published in the Journal of Materials Processing Technology indicates that cold forging can reduce production time by up to 50%, leading to lower labor costs and higher throughput. Additionally, the process generates less waste material, contributing to more sustainable manufacturing practices.
**Tips:** When considering cold forging for your production needs, evaluate the specific material properties required for your application to maximize strength and durability. Additionally, investing in high-quality dies can further enhance the efficiency and precision of the cold forging process, ultimately improving your bottom line.