Leave Your Message
-
Phone
-
E-mail
The importance of Forged Steel Parts in manufacturing cannot be overstated. A recent industry report from Smith & Associates states that forged components are crucial for durability and strength in various applications. According to industry expert Dr. Jane Holloway, "Forged Steel Parts provide unmatched resilience in extreme environments." This demonstrates the value and necessity of these components in engineering sectors.
In 2022, the global market for forged steel was valued at approximately $30 billion, reflecting a growing demand. Companies are now seeking effective solutions to produce high-quality parts quickly. However, challenges remain in achieving consistent quality during the forging process. It’s crucial to adopt better technologies and methods to enhance reliability.
Forged Steel Parts are often underappreciated despite their significant role. Recognizing their contributions can lead to improved manufacturing practices. Industry leaders must focus on innovation while addressing existing gaps. Only then can the true potential of forged steel be realized.
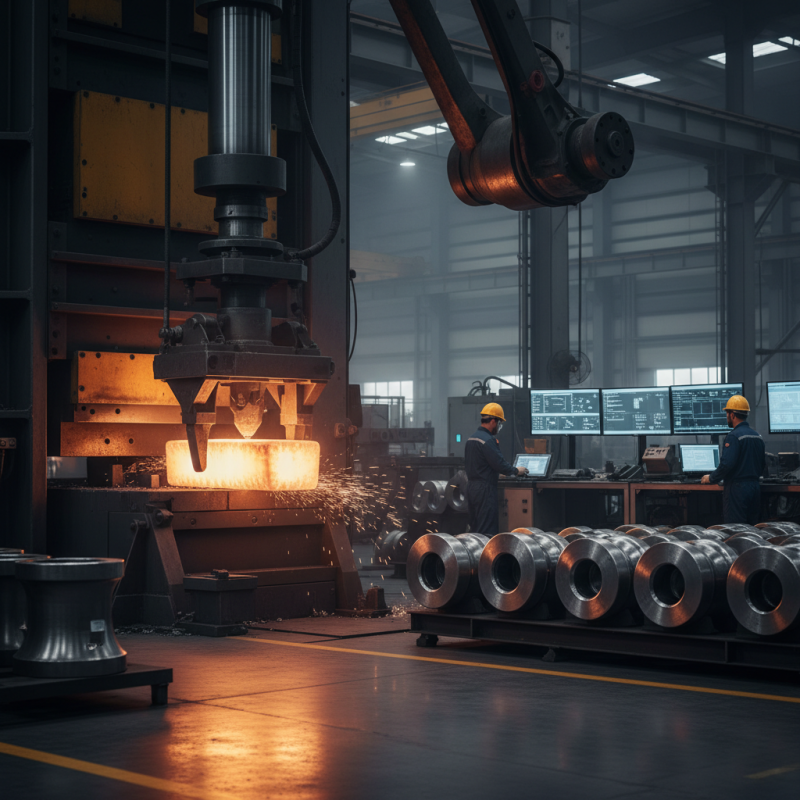


The forging process is essential in manufacturing forged steel parts. It involves shaping metal using compressive forces. This method can create parts with enhanced strength and durability. The process generally starts with heating the steel. The heated metal becomes malleable and easier to mold.
Once heated, the metal is placed in a die. Then, it is subjected to mechanical forces from hammers or presses. This creates a specific shape. However, achieving precision can be challenging. Not all parts turn out perfect. Occasional defects like cracks or inconsistencies can occur during forging. These issues need careful monitoring and adjustment.
After forging, parts often undergo additional processes. They may be machined or heat-treated to meet specifications. These steps ensure parts perform well in their intended applications. Understanding the forging process helps manufacturers improve quality control. It can lead to better production methods and enhanced product performance. Focusing on these factors is crucial for achieving excellence.
Forged steel parts are essential in various manufacturing sectors due to their key properties:
strength, durability, and reliability. Understanding these properties can significantly influence production outcomes. Forged steel exhibits superior tensile strength, often
reaching 200 ksi (kilopounds per square inch) and beyond. This strength makes forged components ideal for high-stress applications, such as automotive and aerospace industries.
Durability also stands out. Forged steel has fewer internal defects compared to cast steel, which enhances its resistance to wear and fatigue. Data shows that forged components can last up to
30% longer than their cast counterparts in demanding scenarios. On the reliability front, forged steel maintains consistent performance under variable loads, making it a
trusted choice in critical applications.
However, there are challenges. The forging process requires precise temperature control and skilled labor to minimize defects. Even minor variations can lead to failures.
Instances of unexpected fractures can arise if proper forging techniques are not adhered to. Manufacturers must constantly evaluate their processes to ensure quality control, emphasizing the need for continual improvements in mechanical processes.
This attention to detail is vital in cultivating the desired strength and reliability often associated with forged steel parts.
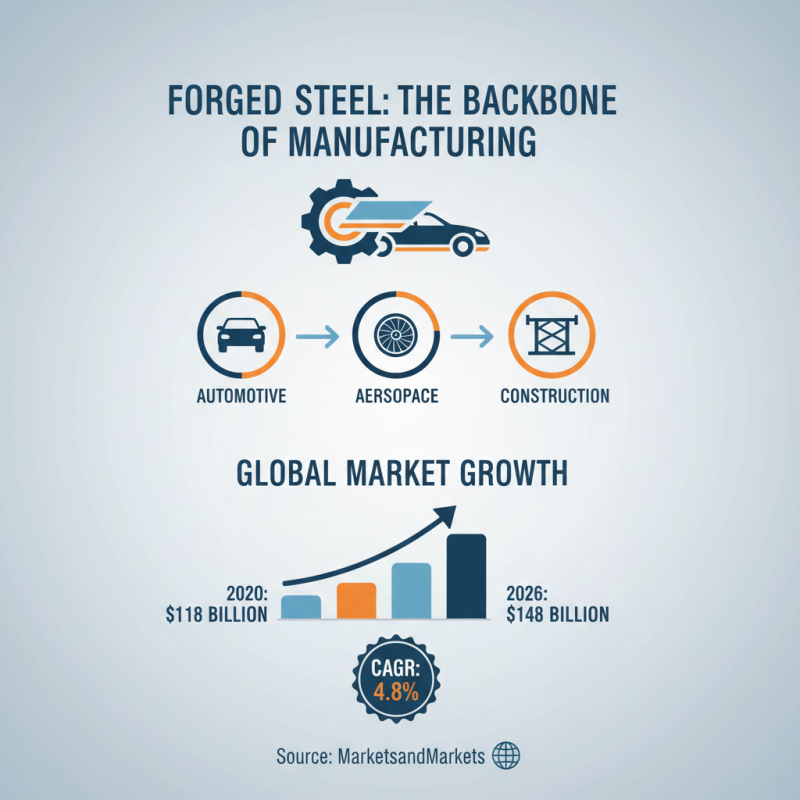
In the manufacturing sector, forged steel parts play a crucial role. Industries like automotive, aerospace, and construction rely heavily on these components. A study by MarketsandMarkets indicates that the global forged steel market is projected to reach $148 billion by 2026, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.8%. This shows an increasing demand across various sectors.
Automotive applications represent a significant portion, accounting for over 30% of the total market. Forged components are vital for engine parts and chassis. This demand can be attributed to their strength and ability to withstand high stress. Moreover, the aerospace industry is using forged steel for landing gear and structural components. According to the Aerospace Industries Association, the demand in this sector is expected to grow by 5% annually over the next five years.
However, challenges persist in the forging process. There are inconsistencies in material quality and design limitations that could impact final applications. Many manufacturers are now investing in advanced technologies to enhance precision. In addition, some smaller companies struggle with the environmental impacts of forging processes. These issues highlight the need for continuous improvement and innovation in the forged steel sector.
The demand for forged steel products is rising in 2023. Industries such as automotive and aerospace are key drivers. These sectors require high-strength, durable components. This has led to significant growth in the forged steel market. Companies are investing in advanced manufacturing technologies to meet this demand.
However, challenges persist. Supply chain disruptions can impact production timelines. Many manufacturers face rising raw material costs, which puts pressure on pricing. Additionally, the need for skilled labor in forging processes remains a concern. Achieving precision in forging requires expertise. The quest for innovation often clashes with these real-world issues.
Market trends indicate a move towards sustainability. Eco-friendly practices are becoming essential. Manufacturers are exploring ways to reduce waste and energy consumption. Adapting to these trends can be difficult. Balancing cost and sustainability is a complex task. Yet, addressing these challenges can lead to a more resilient industry.
In the forging industry, quality control standards are crucial for optimal performance. These standards ensure that forged steel parts maintain their durability and strength. According to a recent report by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), nearly 75% of forging defects stem from inadequate inspection processes.
Effective quality control involves multiple stages. Initial assessments often include material testing and dimensional verification. However, many manufacturers still overlook thorough audits. A lack of proper inspection can lead to significant failures in performance. Research indicates that defects can reduce product lifespan by 30% or more, impacting overall safety and reliability.
Moreover, using advanced technologies like non-destructive testing (NDT) can enhance quality assurance. A study by the International Journal of Manufacturing Technology suggests that companies implementing NDT methods see a 20% increase in defect detection rates. Despite advancements, some players in the industry resist updates to quality protocols. Reflecting on these practices may be essential for advancing standards across the sector.